
What is CD-ROM
CD-ROM (Compact Disc-Read-Only Memory) is an optical disk use for storing large amount of data, the most common is 650 Megabytes. CD-ROMs are popularly used to distribute computer software, including games and multimedia applications, though any data can be stored (up to the capacity limit of a disc).

What is CD-RW
CD-RW(Compact Disc ReWritable) is a rewritable optical disc. It enables you to write over it many times.

What is DVD-ROM
DVD-ROM is an optical disc storage that is capable to store atleast 47.7gigabytes.
DVD-ROM has data which can only be read but cannot be written over. It has the same size and form with CD-ROM

What is DVD-RW
DVD-RW is a rewritable optical disc which has a typical storage of 4.7 gigabytes. Its primary advantage is its ability to erase and rewrite data. It is most suitable for volatile data such as back ups or collection of files. One advantage also of using this disc is if there are writing error in recording data, the disc can be reused again by erasing the faulty data.

What is Hard Disk Drive
Hard Disk Drive is the mechanism that controls the positioning, reading, and writing of the hard disk, which furnishes the largest amount of data storage for the PC. Although the hard disk drive and the hard disk are not the same thing, they are packaged as a unit and so either term is sometimes used to refer to the whole unit.
There are several interface standards for passing data between a hard disk and a computer. The most common are IDE and SCSI. ?
A single hard disk/drive usually consists of several platters. Each platter requires two read/write heads, one for each side. All the read/write heads are attached to a single access arm so that they cannot move independently. Each platter has the same number of tracks, and a track location that cuts across all platters is called a cylinder. For example, a typical 84 megabyte hard disk for a PC might have two platters (four sides) and 1,053 cylinders
A hard disk/drive unit comes with a set rotation speed varying from 4500 to 7200 rpm. Disk access time is measured in milliseconds. Although the physical location can be identified with cylinder, track, and sector locations, these are actually mapped to a logical block address (LBA) that works with the larger address range on today’s hard disks.

What is Keyboard
A Keyboard is a primary input device that is used mainly for inputting text. Its key-arrangement was patterned from and electronic and mechanical typewriter.
The standard layout of letters, numbers, and punctuation is known as a QWERTY keyboard because the first six keys on the top row of letters spell QWERTY. The QWERTY keyboard was designed in the 1800s for mechanical typewriters and was actually designed to slow typists down to avoid jamming the keys. Another keyboard design, which has letters positioned for speed typing, is the Dvorak keyboard.
There is no standard computer keyboard, although many manufacturers imitate the keyboards of PCs. There are actually three different PC keyboards: the original PC keyboard, with 84 keys; the AT keyboard, also with 84 keys; and the enhanced keyboard, with 101 keys. The three differ somewhat in the placement of function keys, the Control key, the Return key, and the Shift keys.
In addition to these keys, IBM keyboards contain the following keys: Page Up, Page Down, Home, End, Insert, Pause, Num Lock, Scroll Lock, Break, Caps Lock, Print Screen.
There are several different types of keyboards for the Apple Macintosh. All of them are called ADB keyboards because they connect to the Apple Desktop bus (ADB). The two main varieties of Macintosh keyboards are the standard keyboard and the extended keyboard, which has 15 additional special-function keys.

What is LCD Monitor
LCD Monitors are commonly used in notebook computers and now are most popular for flat panel desktop monitors. It is a flat panel display device that uses rod-shaped molecules called liquid crystals that flow like liquid and bend light. It is often utilized in battery-powered electronic devices because it uses very small amounts of electric power.

What is Memory or RAM
Memory or RAM is the temporary working memory that your computer uses to perform calculations and manipulate files. When you open a document, it is copied from the hard drive into RAM. As you and your word processor work on the file, the modified copy exists only in RAM. When you save the file, it is copied from RAM back to the hard drive, or permanent storage. It is also the place in a computer where the operating system, application programs, and data in current use are kept so that they can be quickly reached by the computer’s processor.
Two basic types of RAM
Dynamic RAM – the more common type but need to be refreshed thousands of times every seconds because its made up of millions of transistors and capacitors.
Static RAM – RAM does not need to be refreshed, which makes it faster; but it is also more expensive than dynamic RAM. It is mainly used in cache.
Other types of RAM
FPM DRAM: Fast page mode dynamic random access
EDO DRAM: Extended data-out dynamic random access memory
SDRAM: Synchronous dynamic random access memory
DDR SDRAM: Double data rate synchronous dynamic RAM
RDRAM: Rambus dynamic random access
Credit Card Memory
PCMCIA Memory Card:
CMOS RAM:
VRAM: VideoRAM

What is a Modem
A Modem which comes from the word “Modulator/Demodulator” is a device that modulates outgoing digital signal from computer or any digital devices into an analog signal to transmit trough cable or telephone lines and demodulates incoming analog signal from cable or telephones lines into digital signal to be used for any digital devices such as computer
In its basic explanation, a modem is a device that allows you to send and receive information with your computer through phone lines. You could send photos to your friends and receive e-mail messages from your family.
Modems are generally classified by the amount of data they can send in a given time, normally measured in bits per second, or “bps”. They can also be classified by Baud, the number of distinct symbols transmitted per second; these numbers are directly connected, but not necessarily in linear fashion.
Faster modems are used by Internet users every day, notably cable modems and ADSL modems. In telecommunications, “radio modems” transmit repeating frames of data at very high data rates over microwave radio links. Some microwave modems transmit more than a hundred million bits per second. Optical modems transmit data over optical fibers. Most intercontinental data links now use optical modems transmitting over undersea optical fibers. Optical modems routinely have data rates in excess of a billion (1×109) bits per second. One kilobit per second (kbit/s or kb/s or kbps) as used in this article means 1000 bits per second and not 1024 bits per second.

What is a Motherboard
A motherboard is a printed circuit board that is the foundation of a computer and allows the CPU, RAM, and all other computer hardware components to function with each other. It is also known as a mainboard, baseboard, system board, and logic board.
A typical motherboard provides attachment points for one or more of the following: CPU, graphics card, sound card, hard disk controller, memory (RAM), and external peripheral devices.
A motherboard can come in many configurations to fit different needs and budgets. At its most basic, it comes with several interfaces for necessary components and a BIOS chip set to control setup of the motherboard. Many computer enthusiasts favor one type of BIOS over another and will choose a motherboard partially based on the BIOS manufacturer. For example, many gamers prefer the Nvidia BIOS as it is rated as one of the best for graphics applications.
An equally important feature of the motherboard is the type of CPU it will support. Some motherboards support AMD CPUs, while others support Intel processors. Within the manufacturer’s categories, there are different grades of CPUs. An AMD 64-bit processor requires a different CPU socket than an AMD 32-bit processor. Thus, if purchasing parts independently, one must decide on the CPU before choosing the motherboard to ensure compatibility.
Another important consideration is the amount and type of RAM the motherboard will support. It is always best to buy a board that supports more RAM than currently needed. If new technology for RAM chips is available, getting a board that supports the newer chips will help future-proof the investment..
The number of PCI slots varies from motherboard to motherboard, as do other interfaces like the number of SATA ports, differing RAID abilities, and USB and Firewire ports. As mentioned prior, sound and video capability might be built-in, though purists generally prefer to disable internal video and sound and add superior third party cards. A motherboard also comes in one of a few standard footprints or sizes. This figures in when purchasing the system case. Along these lines, many motherboard manufacturers recommend particular power supplies that have been tested with the board.
Though building a computer used to be somewhat challenging, today most motherboards are color-coded with controllers built-in, making it very easy to build a computer from scratch. The only time consuming aspect is investigating which hardware will best suit your needs while fitting into your budget. Once the CPU and motherboard is chosen, RAM is somewhat determined by the board itself. Hard drives, an optical disk, a video card, a sound card and a floppy round out the basics.
Most motherboard today was designed for IBM compatible computers which holds over 96% of the computers in the market today.

What is a Mouse
A mouse is a small device that a computer user pushes across a desk surface in order to point to a place on a display screen and to select one or more actions to take from that position.
There are three basic types of mice:
1. mechanical:Has a rubber or metal ball on its underside that can roll in all directions. Mechanical sensors within the mouse detect the direction the ball is rolling and move the screen pointer accordingly.
2. optomechanical:Same as a mechanical mouse, but uses optical sensors to detect motion of the ball.
3. optical:Uses a laser to detect the mouse’s movement. You must move the mouse along a special mat with a grid so that the optical mechanism has a frame of reference. Optical mice have no mechanical moving parts. They respond more quickly and precisely than mechanical and optomechanical mice, but they are also more expensive.
Mice connect to PCs in one of several ways:
1. Serial mice connect directly to an RS-232C serial port or a PS/2 port. This is the simplest type of connection.
2. PS/2 mice connect to a PS/2 port.
3. USB mice.
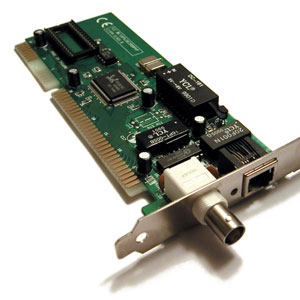
What is a Network Card
Network Card also known as Network Interface Card or NIC, network adapter, LAN Adapter, is a printed circuit board containing the necessary hardware used to connect a computer to a network or other computer. It provide a dedicated, full-time connection to a network.
In Seven Layer of OSI Model, Network Card falls both to Physical layer and Data Link layer device. It provides physical access to a networking medium and provides a low-level addressing system through the use of MAC addresses. It allows users to connect to each other either by using cables or wirelessly. It implements the electronic circuitry required to communicate using a specific physical layer and data link layer standard.
Ethernet is the most common network technology that exist. It has achieved near-ubiquity since the mid-1990s. Every Ethernet network card has a unique 48-bit serial number called a MAC address, which is stored in ROM carried on the card. Every computer on an Ethernet network must have a card with a unique MAC address. No two cards ever manufactured share the same address. This is accomplished by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which is responsible for assigning unique MAC addresses to the vendors of network interface controllers.
There are four techniques used to transfer data, the network card may use one or more of these techniques.
• Polling is where the microprocessor examines the status of the peripheral under program control
• Programmed I/O is where the microprocessor alerts the designated peripheral by applying its address to the system’s address bus.
• Interrupt-driven I/O is where the peripheral alerts the microprocessor that it’s ready to transfer data.
• DMA is where the intelligent peripheral assumes control of the system bus to access memory directly. This removes load from the CPU but requires a separate processor on the card.
A network card typically has a twisted pair, BNC, or AUI socket where the network cable is connected, and a few LEDs to inform the user of whether the network is active, and whether or not there is data being transmitted on it. The Network Cards are typically available in 10/100/1000 Mbit/s(Mbit/s). This means they can support a transfer rate of 10 or 100 or 1000 Megabits per second.
Most computers nowadays comes with a built-in network card on their motherboard.

What is Printer
An external hardware device responsible for taking computer data and generating a hard copy of that data. Printers are one of the most used peripherals on computers and are commonly used to print text, images, and/or photos.
Many printers are primarily used as local computer peripherals, and are attached by a printer cable to a computer which serves as a document source. Some printers, commonly known as network printers, have built-in network interfaces (typically wireless or Ethernet), and can serve as a hardcopy device for any user on the network. Individual printers are often designed to support both local and network connected users at the same time. Many modern printers can directly interface to electronic media such as memory sticks or memory cards, or to image capture devices such as digital cameras, scanners; some printers are combined with a scanners and/or fax machines in a single unit.
There are several types of printers
• daisy-wheel Similar to a ball-head typewriter, this type of printer has a plastic or metal wheel on which the shape of each character stands out in relief. A hammer presses the wheel against a ribbon, which in turn makes an ink stain in the shape of the character on the paper. Daisy-wheel printers produce letter-quality print but cannot print graphics.
• dot-matrix: Creates characters by striking pins against an ink ribbon. Each pin makes a dot, and combinations of dots form characters and illustrations
• ink-jet: Sprays ink at a sheet of paper. Ink-jet printers produce high-quality text and graphics
• laser: Uses the same technology as copy machines. Laser printers produce very high quality text and graphics
• LCD & LED: Similar to a laser printer, but uses liquid crystals or light-emitting diodes rather than a laser to produce an image on the drum.
• line printer: Contains a chain of characters or pins that print an entire line at one time. Line printers are very fast, but produce low-quality print.
• thermal printer: An inexpensive printer that works by pushing heated pins against heat-sensitive paper. Thermal printers are widely used in calculators and fax machines.
Printers are also classified by the following characteristics:
• quality of type: The output produced by printers is said to be either letter quality (as good as a typewriter), near letter quality, or draft quality. Only daisy-wheel, ink-jet, and laser printers produce letter-quality type. Some dot-matrix printers claim letter-quality print, but if you look closely, you can see the difference.
• speed: Measured in characters per second (cps) or pages per minute (ppm), the speed of printers varies widely. Daisy-wheel printers tend to be the slowest, printing about 30 cps. Line printers are fastest (up to 3,000 lines per minute). Dot-matrix printers can print up to 500 cps, and laser printers range from about 4 to 20 text pages per minute.
• impact or non-impact: Impact printers include all printers that work by striking an ink ribbon. Daisy-wheel, dot-matrix, and line printers are impact printers. Non-impact printers include laser printers and ink-jet printers. The important difference between impact and non-impact printers is that impact printers are much noisier.
• graphics: Some printers (daisy-wheel and line printers) can print only text. Other printers can print both text and graphics.
• fonts : Some printers, notably dot-matrix printers, are limited to one or a few fonts. In contrast, laser and ink-jet printers are capable of printing an almost unlimited variety of fonts. Daisy-wheel printers can also print different fonts, but you need to change the daisy wheel, making it difficult to mix fonts in the same document.
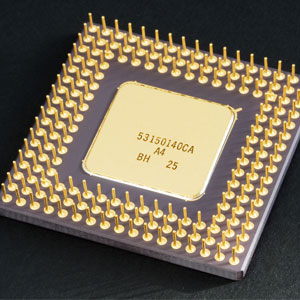
What is a Processor
The processor is the brain of the computer. It handles all the processes and transactions done by a personal computer. CPU and processor are used interchangeably. CPU or processor is housed in a single chip called microprocessor.
Components of CPU:
• The arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which performs arithmetic and logical operations.
• The control unit (CU), which extracts instructions from memory and decodes and execute them, calling on the ALU when necessary.
CPU was housed inside a silicon chip called microprocessor. Microprocessor has three basic characteristics which are:
• Instruction set – The set of instructions that the microprocessor can execute.
• Bandwidth – The number of bits processed in a single instruction.
• Clock speed – Given in megahertz (MHz or GHz), the clock speed determines how many instructions per second the processor can execute.

What is a Scanner
A Scanner is a computer peripheral device that allows a user to take an image and/or text printed on paper and convert it into a digital file, allowing the computer to read and/or display the scanned object. A scanner is commonly connected to a computer USB, Firewire, Parallel or SCSI port.
There are several types of SCANNER:
• Flatbed scanner – . It consists of a board on which you lay books, magazines, and other documents that you want to scan. It looks like a photocopy machine. They are also called desktop scanners, They are the most versatile and commonly used scanners.
• Sheet-Feed scanner – it is large scanner which you can feed papers. It is also called desktop scanners. These scanners are excellent for loose sheets of paper, but they are unable to handle bound documents. It scanner looks a lot like a small portable printer.
• Overhead scanners (also called copyboard scanners) look somewhat like overhead projectors. You place documents face-up on a scanning bed, and a small overhead tower moves across the page.
• Handheld scanners use the same basic technology as a flatbed scanner, but rely on the user to move them instead of a motorized belt. This type of scanner typically does not provide good image quality. However, it can be useful for quickly capturing text.
• Drum scanners are used by the publishing industry to capture incredibly detailed images. They use a technology called a photomultiplier tube (PMT). In PMT, the document to be scanned is mounted on a glass cylinder. At the center of the cylinder is a sensor that splits light bounced from the document into three beams. Each beam is sent through a color filter into a photomultiplier tube where the light is changed into an electrical signal.

What is Sound Card
Also known as a sound board or an audio card, a sound card is an expansion card or integrated circuit that provides a computer with the ability to produce sound that can be heard by the usercanner is commonly connected to a computer USB, Firewire, Parallel or SCSI port.
The sound card’s four main functions are: as a synthesizer (generating sounds), as a MIDI interface, analog-to-digital conversion (used, for example, in recording sound from a microphone), and digital-to-analog conversion (used, for example, to reproduce sound for a speaker). The three methods of sound synthesis are through frequency modulation (FM) technology, wavetable, and physical modeling
FM synthesis is the least expensive and least effective method. Sounds are simulated by using algorithms to create sine waves that are as close to the sound as possible. For example, the sound of a guitar can be simulated, although the result does not really sound very much like a guitar. Wavetable uses actual, digitally recorded sound samples stored on the card for the highest performance. Physical modeling is a new type of synthesizing, in which sounds are simulated through a complex programming procedure. Some
sound cards can also have sounds downloaded to them.
Some sound cards have 3-D capabilities enabled by processors on the card that use mathematical formulas to create greater depth, complexity, and realism of sound. High quality audio can be produced through a system that uses the Universal Serial Bus (USB) and does not require a sound card.

What is UPS
Uninterruptible Power Supply, UPS is a hardware device that provides a backup power source in case of a power outage (blackout), brownout, or a surge in power. A UPS provides enough power for the computer or computers to shut down properly or to remain up during a temporary power outage. Typically, a UPS keeps a computer running for several minutes after a power outage, enabling you to save data that is in RAM and shut down the computer gracefully.
Many UPSs now offer a software component that enables you to automate backup and shut down procedures in case there’s a power failure while you’re away from the computer. There are two distinct types of UPS: off-line and line-interactive (also called on-line).
An off-line UPS remains idle until a power failure occurs, and then switches from utility power to its own power source, almost instantaneously. An on-line UPS continuously powers the protected load from its reserves (usually lead-acid batteries), while simultaneously replenishing the reserves from the AC power.
The on-line type of UPS, in addition to providing protection against complete failure of the utility supply, provides protection against all common power problems, and for this reason it is also known as a power conditioner and a line conditioner.

What is Video Card
Also known as a graphics card, graphic adapter, video board, video controller, video adapter is an internal circuit board that allows a display device, such as a monitor, to display images from the computer. It operates on similar principles as a sound card or other peripheral devices. The term is usually used to refer to a separate, dedicated expansion card that is plugged into a slot on the computer’s motherboard.
Video cards are typically installed in either the PCI, AGP or PCIe slots in the back of a computer. Most computers come with a video card installed in one of these slots, which means it can be upgraded at a later time.
Most video cards support the OpenGL and DirectX libraries. These libraries include commands for manipulating graphics that programmers can include in their code. Some of these commands may include moving or rotating an object, morphing polygons, or casting light and creating shadows. By using standard OpenGL or DirectX functions, it makes it easier for developers to create graphically-oriented programs. Of course, it also makes it necessary for the computer to include a supported video card in order for the program to run.

What is Video Projector
A hardware device that enables an image, such as a computer screen, to be projected onto a flat surface. All video projectors use a very bright light to project the image, and most modern ones can correct any curves, blurriness, and other inconsistencies through manual settings. Video projectors are widely used for video conference, room presentations, classroom training, and home theatre applications.
Common display resolutions for a portable projector include SVGA (800×600 pixels), XGA (1024×768 pixels), 720p (1280×720 pixels), and 1080p (1920×1080 pixels).
The cost of a device is not only determined by its resolution, but also by its light output, acoustic noise output, contrast, and other characteristics. While most modern projectors provide sufficient light for a small screen at night or under controlled lighting such as in a basement with no windows, a projector with a higher light output (measured in lumens, abbreviated “lm”) is required for a larger screen or a room with a higher amount of ambient light. A rating of 1000 to 1500 ANSI lumens or lower is suitable for smaller screens with controlled lighting or low ambient light. Between 1500 and 3000 lm is suitable for medium-sized screens with some ambient light or dimmed light. Over 3000 lm is appropriate for very large screens in a large room with no lighting control (for example, a conference room). Projected image size is important; because the total amount of light does not change, as size increases, brightness decreases. Image sizes are typically measured in linear terms, diagonally, obscuring the fact that larger images require much more light (proportional to the image area, not just the length of a side). Increasing the diagonal measure of the image by 25 % reduces the image brightness by 35 per cent; an increase of 41 per cent reduces brightness by half.

What is Webcam
A camera connected to a computer or server that allows anyone connected to the internet to view still pictures or motion video of a user. The term webcam is also used to describe the low-resolution digital video cameras designed for such purposes, but which can also be used to record in a non-real-time fashion. . Webcam software typically captures the images as JPEG or MPEG files and uploads them to the Web server either continuously or at regular intervals. Videoconferencing cameras typically take the form of a small camera connected directly to a PC. Analog cameras are also sometimes used (often of the sort used for closed-circuit television), connected to a video capture card and then directly or indirectly to the internet.















